AGENDA
The formation of the ADN is timely and is directly related to the UN’s current ambitions. In 2015, the UN’s ‘Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030’ adopted seven Global Targets, of which the first two Targets are:
(a) Substantially reduce global disaster mortality by 2030, aiming to lower average per 100,000 global mortality rate in the decade 2020-2030 compared to the period 2005-2015;
(b) Substantially reduce the number of affected people globally by 2030, aiming to lower the average global figure per 100,000 in the decade 2020 -2030 compared to the period 2005-2015.”
In 2015, the UN also revised the Millennium Development Goals, currently known as the ‘Sustainable Development Goals 2015-2030’. There are 17 Goals, of which the most relevant to the ADN are Goal 1 (No Poverty), Goal 2 (Zero Hunger), Goal 3 (Good Health and Well Being), Goal 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), Goal 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) and Goal 17 (Partnerships for the Goals). More than 185 UN Member States have ratified the UN’s Sendai and the Sustainable Development Goals; hence, they are extremely important frameworks in low and middle-income countries.
Through its agenda of ‘avoidable disaster deaths’ the ADN addresses these goals by gathering evidence to “build the knowledge of government officials at all levels, civil society, communities and volunteers, as well as the private sector, through sharing experiences, [research,] lessons learned, good practices and training and education on disaster risk reduction, including the use of existing training and education mechanisms and peer learning” (UNISDR, 2015, p. 15).
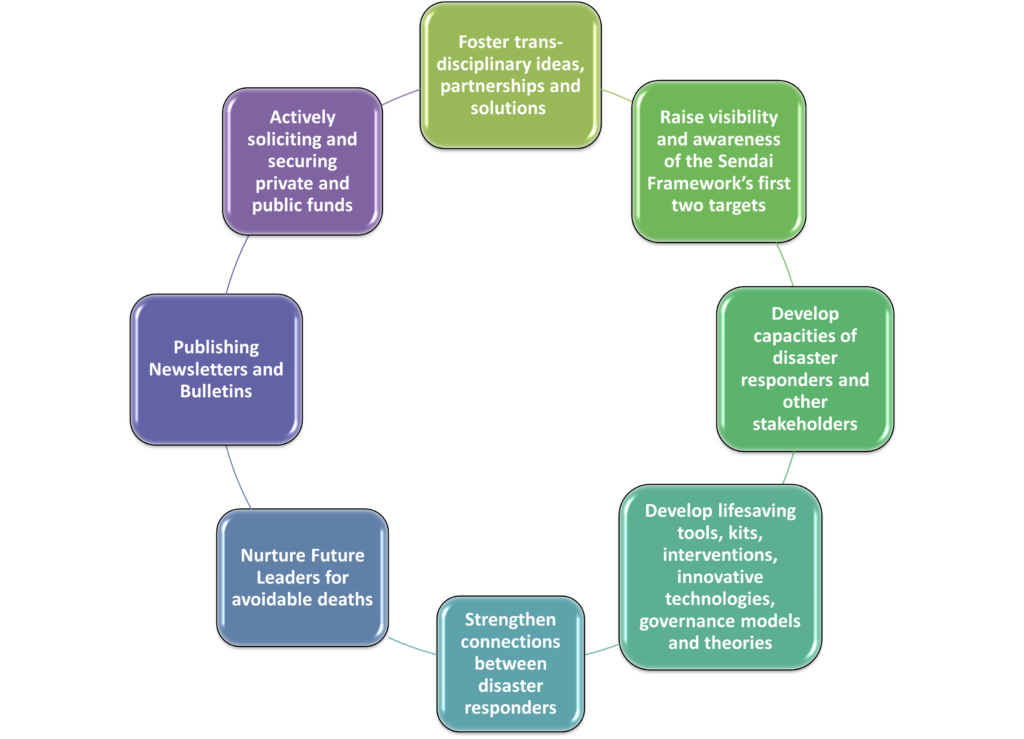
ACTIVITIES
- Foster trans-disciplinary ideas, partnerships and solutions to reduce avoidable disaster deaths and people affected by disasters for sustainable development in low-and middle-income countries, through knowledge exchange events (conferences, symposiums and webinars).
- Raise visibility and awareness of the Sendai Framework’s first two targets, through publications, and knowledge exchange events.
- Develop capacities of disaster responders and other stakeholders, through continuing professional development courses, knowledge exchange events and an information repository.
- Develop lifesaving tools, kits, interventions, innovative technologies, governance models and theories to reduce the burden of maternal mortality, snakebite mortality, drowning mortality during disasters, and tsunami mortality through evidence-based pioneering research on hazards, exposures, vulnerability and risks.
- Strengthen connections between disaster responders, through leveraging existing and promoting novel networking platforms.
- Nurture future leaders for Avoidable Deaths and improve their leadership and employability skills, through expert mentoring and engaging Interns for activities related to 1-5.
- Publishing Newsletter and Bulletins for knowledge exchange; and
- Actively soliciting and securing private and public funds to promote the above activities.
RESEARCH THEMES
- Disaster education.
- Maternal deaths from an unsafe abortion and post-abortion complications.
- Direct and indirect disaster deaths.
- Snakebites deaths.
- Drowning deaths.
GLOBAL CAMPAIGN
On 12 March 2023 we launched a global campaign ‘International Awareness Day for Avoidable Deaths’ (IAD4AD) and the campaign slogan is ‘Disaster Deaths Are Avoidable’. This is a public engagement global campaign and by engaging with different disaster actors and organisations and citizens of the global community we aim to raise the visibility of avoidable disaster deaths for systemic change and development.

DOWNLOADABLE RESOURCES
Information Booklet
Flyer
Glossary of Terms
INNOVATIONS
Knowledge-Exchange Network
The Knowledge-Exchange Network (KEN) platform (work in progress) is also referred to as a Knowledge-Sharing Network (KSN) in older documents. A KEN would foster i) dialogue and discussions within and across stakeholder locations; ii) coordination, cooperation, and communication amongst stakeholders for resource-sharing and response at local levels; iii) identify scope for transformative interdisciplinary research; and iv) improve the capacity of local stakeholders.
Avoidable Deaths Framework
The Avoidable Deaths Framework (ADF) (work in progress) is a research project that aims to capture the number of avoidable deaths from the effects of COVID-19 and economic lockdown in India (first phase), and how can we reduce disaster deaths that are avoidable. The number of deaths from the effects of COVID-19 is understood through the lens of an ‘avoidable disaster deaths perspective’.
Facility and Crisis Reproductive Health Kits
The Low-budget protocol for Facility Reproductive Health Kit and Crisis Reproductive Health Kit (2021) was a protocol developed for two low-budget reproductive health (RH) kits.
The Facility and Crisis RH Kits are designed for the management of post-abortion complications including incomplete, septic and spontaneous abortion (before and after 12 weeks of missed menstruation). The former Kit is specifically designed to be used during disasters and humanitarian crises at primary, as well as secondary health facilities. The latter Kit is designed to be lightweight so that service providers can carry it to emergency response facilities (e.g., flood-cum-cyclone shelters, safe homes, and refugee camps or any temporary disaster camps). The Kits are designed on the principle of localisation and to save women and girls of reproductive age during disasters and crises.
Integrated Intervention Package RHCC
The Integrated Intervention Package RHCC (2019) is designed to improve the quality and availability of post-abortion care during a major flood at primary health care level with the overall aim of reducing maternal mortality and morbidity (SDG3, Sendai Target A)). The RHCC has three components: i) pre-positioning of Reproductive Health Kit prior to flooding; ii) Capacity building of health workers; and iii) Community awareness raising. The evidence-based RHCC package was first tested in Belkuchi, Bangladesh. The RHCC comes with a Structured Facility Assessment Tool and a Two-Step Checklist Facility Assessment Tool. These tools are designed to assess the capacity of the facilities for sexual and reproductive services including menstrual regulation and post-abortion care during disasters and humanitarian crises.
Systems Failure Approach
The Systems Failure Approach (2018): The research monograph Avoidable Deaths presents systems failure as an analytical tool to explain why deaths occur in disasters and how they may be reduced. The systems failure approach demonstrates that deaths in disasters are socio-technical failures, and that it is by rectifying systems failures and promoting systems alignment that deaths can be prevented.